Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
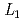 -edge XAFS measurement
-edge XAFS measurementTsuji, Takuya; Matsumura, Daiju; Kobayashi, Toru
SPring-8/SACLA Riyo Kenkyu Seikashu (Internet), 11(4), p.214 - 217, 2023/08
no abstracts in English
Yuan, X.*; Hu, Q.*; Lin, X.*; Zhao, C.*; Wang, Q.*; Tachi, Yukio; Fukatsu, Yuta; Hamamoto, Shoichiro*; Siitari-Kauppi, M.*; Li, X.*
Journal of Hydrology, 618, p.129172_1 - 129172_15, 2023/03
Times Cited Count:0 Percentile:0(Engineering, Civil) Cs NMR chemical shift of clay minerals via machine learning and DFT-GIPAW calculations
Cs NMR chemical shift of clay minerals via machine learning and DFT-GIPAW calculationsOkubo, Takahiro*; Takei, Akihiro*; Tachi, Yukio; Fukatsu, Yuta; Deguchi, Kenzo*; Oki, Shinobu*; Shimizu, Tadashi*
Journal of Physical Chemistry A, 127(4), p.973 - 986, 2023/02
Times Cited Count:1 Percentile:56.86(Chemistry, Physical)The identification of adsorption sites of Cs on clay minerals has been studied in the fields of environmental chemistry. The nuclear magnetic resonance (NMR) experiments allow direct observations of the local structures of adsorbed Cs. The NMR parameters of  Cs, derived from solid-state NMR experiments, are sensitive to the local neighboring structures of adsorbed Cs. However, determining the Cs positions from NMR data alone is difficult. This paper describes an approach for identifying the expected atomic positions of Cs adsorbed on clay minerals by combining machine learning (ML) with experimentally observed chemical shifts. A linear ridge regression model for ML is constructed from the smooth overlap of atomic positions descriptor and gauge-including projector augmented wave (GIPAW) ab initio data. The
Cs, derived from solid-state NMR experiments, are sensitive to the local neighboring structures of adsorbed Cs. However, determining the Cs positions from NMR data alone is difficult. This paper describes an approach for identifying the expected atomic positions of Cs adsorbed on clay minerals by combining machine learning (ML) with experimentally observed chemical shifts. A linear ridge regression model for ML is constructed from the smooth overlap of atomic positions descriptor and gauge-including projector augmented wave (GIPAW) ab initio data. The  Cs chemical shifts can be instantaneously calculated from the Cs positions on any clay layers using ML. The inverse analysis from the ML model can derive the atomic positions from experimentally observed chemical shifts.
Cs chemical shifts can be instantaneously calculated from the Cs positions on any clay layers using ML. The inverse analysis from the ML model can derive the atomic positions from experimentally observed chemical shifts.
Tsuji, Takuya; Matsumura, Daiju; Kobayashi, Toru; Yaita, Tsuyoshi
SPring-8/SACLA Riyo Kenkyu Seikashu (Internet), 11(1), p.15 - 18, 2023/02
no abstracts in English
Tachi, Yukio; Sato, Tomofumi*; Akagi, Yosuke*; Kawamura, Makoto*; Nakane, Hideji*; Terashima, Motoki; Fujiwara, Kenso; Iijima, Kazuki
Science of the Total Environment, 724, p.138098_1 - 138098_11, 2020/07
Times Cited Count:13 Percentile:57.17(Environmental Sciences)To understand and predict radiocesium transport behaviors in the environment, highly contaminated sediments from Ukedo and Odaka rivers around the Fukushima Daiichi Nuclear Power Plant were investigated systematically focusing on key factors controlling radiocesium sorption and fixation, including particle size, clay mineralogy and organic matter.
Tachi, Yukio; Sato, Tomofumi*; Takeda, Chizuko*; Ishidera, Takamitsu; Fujiwara, Kenso; Iijima, Kazuki
Science of the Total Environment, 724, p.138097_1 - 138097_10, 2020/07
Times Cited Count:9 Percentile:43.42(Environmental Sciences)To understand and predict radiocesium transport behaviors in the environment, sorption and fixation behaviors of radiocesium on river sediments from Ukedo and Odaka rivers around the Fukushima Daiichi Nuclear Power Plant were investigated systematically focusing on Cs sorption and fixation mechanisms and their relationship with Cs concentrations and sediment properties including clay mineralogy and organic matter.
Yin, X.; Zhang, L.*; Meng, C.*; Inaba, Yusuke*; Wang, X.*; Nitta, Ayako; Koma, Yoshikazu; Takeshita, Kenji*
Journal of Hazardous Materials, 387, p.121677_1 - 121677_10, 2020/04
Times Cited Count:12 Percentile:54.1(Engineering, Environmental)Sugiura, Yuki; Suyama, Tadahiro*; Tachi, Yukio
JAEA-Data/Code 2019-022, 40 Pages, 2020/03
Sorption behavior of radionuclides (RNs) in buffer materials, rocks and cementitious materials is one of the key processes in a safe geological disposal. This report focuses on updating of JAEA sorption database (JAEA-SDB) as a basis of integrated approach for the performance assessment (PA)-related distribution coefficient (K ) setting and development of mechanistic sorption models. K
) setting and development of mechanistic sorption models. K data and their quality assurance (QA) results were updated by focusing on the following systems as potential needs extracted from our recent activities on the K
data and their quality assurance (QA) results were updated by focusing on the following systems as potential needs extracted from our recent activities on the K setting and development of mechanistic models, i.e., clay minerals, sedimentary rocks and cementitious materials. As a result, 6,702 K
setting and development of mechanistic models, i.e., clay minerals, sedimentary rocks and cementitious materials. As a result, 6,702 K data from 60 references were added and the total number of K
data from 60 references were added and the total number of K values in JAEA-SDB reached 69,679. The QA/classified K
values in JAEA-SDB reached 69,679. The QA/classified K data reached about 72% for all K
data reached about 72% for all K data in JAEA-SDB.
data in JAEA-SDB.
Collaborative Laboratories for Advanced Decommissioning Science; Osaka University*
JAEA-Review 2019-029, 36 Pages, 2020/02
JAEA/CLADS, had been conducting the Center of World Intelligence Project for Nuclear Science/Technology and Human Resource Development (hereafter referred to "the Project") in FY2018. The Project aims to contribute to solving problems in nuclear energy field represented by the decommissioning of the Fukushima Daiichi Nuclear Power Station, Tokyo Electric Power Company Holdings, Inc. For this purpose, intelligence was collected from all over the world, and basic research and human resource development were promoted by closely integrating/collaborating knowledge and experiences in various fields beyond the barrier of conventional organizations and research fields. The sponsor of the Project was moved from the Ministry of Education, Culture, Sports, Science and Technology to JAEA since the newly adopted proposals in FY2018. On this occasion, JAEA constructed a new research system where JAEA-academia collaboration is reinforced and medium-to-long term research/development and human resource development contributing to the decommissioning are stably and consecutively implemented. Among the adopted proposals in FY2018, this report summarizes the research results of the "Development of Gel Filler that Facilitates Fuel Debris Retrieval". When gel materials such as polymer, silicate and clay minerals with adjusted viscosity are used in the process of debris retrieval, the gel would not leak down from the damaged parts, resulting in the reduction of surrounding air dose rate. In addition, gel materials can reduce the diffusion and scattering of dust that is produced by cutting. For these reasons, we propose a method where inside of a containment vessel is filled by gel materials in order to simplify the debris retrieval.
 Cs in organic layer and mineral soil in Japanese forests; Four-year observation and model analysis
Cs in organic layer and mineral soil in Japanese forests; Four-year observation and model analysisMuto, Kotomi; Atarashi-Andoh, Mariko; Matsunaga, Takeshi*; Koarashi, Jun
Journal of Environmental Radioactivity, 208-209, p.106040_1 - 106040_10, 2019/11
Times Cited Count:13 Percentile:49.32(Environmental Sciences)Vertical distributions of  Cs in the soil profile were observed at five forest sites with different vegetation types for 4.4 years after the Fukushima Dai-ichi Nuclear Power Plant accident, and
Cs in the soil profile were observed at five forest sites with different vegetation types for 4.4 years after the Fukushima Dai-ichi Nuclear Power Plant accident, and  Cs migration in the organic layer and mineral soil was analyzed based on a comparison of models and observations. Cesium-137 migration from the organic layer was faster than that observed in European forests, suggesting that the mobility and bioavailability of
Cs migration in the organic layer and mineral soil was analyzed based on a comparison of models and observations. Cesium-137 migration from the organic layer was faster than that observed in European forests, suggesting that the mobility and bioavailability of  Cs could be suppressed rapidly in Japanese forests. The diffusion coefficients of
Cs could be suppressed rapidly in Japanese forests. The diffusion coefficients of  Cs in the mineral soil were estimated to be 0.042-0.55 cm
Cs in the mineral soil were estimated to be 0.042-0.55 cm y
y , which were roughly comparable with those of European forest soils affected by the Chernobyl Nuclear Power Plant accident. Model predictions indicated
, which were roughly comparable with those of European forest soils affected by the Chernobyl Nuclear Power Plant accident. Model predictions indicated  Cs mainly distributed in the surface mineral soil at 10 years after the accident. It suggest that the
Cs mainly distributed in the surface mineral soil at 10 years after the accident. It suggest that the  Cs deposited onto Japanese forest ecosystems will be retained in the surface layers of mineral soil for a long time.
Cs deposited onto Japanese forest ecosystems will be retained in the surface layers of mineral soil for a long time.
Nohara, Tsuyoshi; Uno, Masaoki*; Tsuchiya, Noriyoshi*
Geofluids, 2019, p.6053815_1 - 6053815_16, 2019/08
Times Cited Count:3 Percentile:29.93(Geochemistry & Geophysics)Amphibole-plagioclase thermometry was applied to estimate the temperature of a glassy vein as approximately 700. The results of observations of the rock core revealed that of supercritical fluid flow was microfracture filling with hornblende and plagioclase. The current high permeability was recognized to be microfracture network. A high-angle fracture of chlorite filling in combination with an open fracture was recognized as characteristics of a high-permeability type.
Okuchi, Takuo*; Tomioka, Naotaka*; Purevjav, N.*; Shibata, Kaoru
Journal of Applied Crystallography, 51, p.1564 - 1570, 2018/12
Times Cited Count:2 Percentile:20.9(Chemistry, Multidisciplinary)It is demonstrated that quasielastic neutron scattering (QENS) is a novel and effective method to analyse atomic scale hydrogen transport processes occurring within a mineral crystal lattice. The method was previously characterized as sensitive for analysing the transport frequency and distance of highly diffusive hydrogen atoms or water molecules in condensed matter. Here are shown the results of its application to analyse the transport of much slower hydrogen atoms which are bonded into a crystal lattice as hydroxyls. Two types of hydrogen transport process were observed in brucite, Mg(OH) : a jump within a single two-dimensional layer of the hydrogen lattice and a jump into the next nearest layer of it. These transport processes observed within the prototypical structure of brucite have direct implications for hydrogen transport phenomena occurring within various types of oxides and minerals having layered structures.
: a jump within a single two-dimensional layer of the hydrogen lattice and a jump into the next nearest layer of it. These transport processes observed within the prototypical structure of brucite have direct implications for hydrogen transport phenomena occurring within various types of oxides and minerals having layered structures.
Sasamoto, Hiroshi; Sato, Hisao*; Arthur, R. C.*
Journal of Geochemical Exploration, 188, p.318 - 325, 2018/05
Times Cited Count:3 Percentile:16.65(Geochemistry & Geophysics)Ammonium is potentially an important constituent of deep groundwater under reducing condition. The retention of cesium by sorption in geological formations may have an important role ensuring the long-term safety of high-level radioactive waste. Cesium sorption will be affected by competing effects due to dissolve cation likely ammonium in groundwater, however. In the present study, a possible reaction to control of ammonium in deep groundwater was evaluated based on the data selected in the Horonobe as a test case in Japan. Results of investigation of mineralogy, thermodynamic evaluation of groundwaters and the Electron Probe Micro Analysis (EPMA) to identify nitrogen distribution on minerals suggest that the clay minerals bearing potassium, particularly smectite, illite and interstratified illite/smectite, appear to control the ammonium concentration in groundwaters by ion exchange reactions. Additionally, the selected groundwaters in the Horonobe seem to resemble to the gas and oil fields groundwater in the screened dataset in Japan in terms of ammonium distribution.
Yaita, Tsuyoshi
Nihon Genshiryoku Gakkai-Shi ATOMO , 59(8), p.441 - 443, 2017/08
, 59(8), p.441 - 443, 2017/08
no abstracts in English
Hirao, Norie; Shimoyama, Iwao; Baba, Yuji; Izumi, Toshinori; Okamoto, Yoshihiro; Yaita, Tsuyoshi; Suzuki, Shinichi
Bunseki Kagaku, 65(5), p.259 - 266, 2016/05
Times Cited Count:4 Percentile:14.35(Chemistry, Analytical)After the Fukushima nuclear plant accident, radiocesium was strongly fixed to clay minerals in the soil. Some dry methods with heating are being developed to remove radiocesium from the soil. In this work, we propose a new dry method that combines heat treatment in vacuum and molten salts to reduce the processing temperature in dry methods. Vermiculite saturated with non-radioactive Cs was heated in vacuum, and Cs contents in the vermiculite were compared before and after heating using X-ray photoelectron spectroscopy. Approximately 40% of cesium were removed by heating at 800 C for three minutes when only vermiculite was heated. Approximately 70% of cesium were removed by heating at 450
C for three minutes when only vermiculite was heated. Approximately 70% of cesium were removed by heating at 450 C for three minutes when vermiculite was heated with NaCl/CaCl
C for three minutes when vermiculite was heated with NaCl/CaCl mixed salts. Based on these results, this method is expected to reduce temperature and increase efficiency on dry methods for cesium removal from clay minerals.
mixed salts. Based on these results, this method is expected to reduce temperature and increase efficiency on dry methods for cesium removal from clay minerals.
Yamaguchi, Tetsuji; Sawaguchi, Takuma; Tsukada, Manabu; Hoshino, Seiichi*; Tanaka, Tadao
Clay Minerals, 51(2), p.279 - 287, 2016/02
Times Cited Count:7 Percentile:24.47(Chemistry, Physical)Alteration of bentonite-cement interfaces and accompanying changes in diffusivity of tritiated water was experimentally investigated using intact hardened cement specimens. The alteration by carbonate solution was accompanied by mineralogical changes at the interface and a decrease in the diffusivity to 70% of the initial value after 180-day period. Another alteration under silicate system contacting hardened cement and compacted bentonite was accompanied by mineralogical changes at the interface and a decrease in the diffusivity to 71% of the initial value after 600-day period. The changes in the diffusivity were much less than those observed for mixed specimens of granulated hardened cement and bentonite where the diffusivity decreased down to 20% of the initial value over 180 days. The results were extrapolated to 15 years under simple assumptions and showed good agreement with those observed in the cement-argillite interface at Tournemire URL. Such an explanation enhances our confidence in our assessment of alteration of cement-bentonite systems and can be a base for using our data and models in long term assessment of radioactive waste disposal.
Ikeda, Takashi; Suzuki, Shinichi; Yaita, Tsuyoshi
Journal of Physical Chemistry A, 119(30), p.8369 - 8375, 2015/07
Times Cited Count:21 Percentile:67.71(Chemistry, Physical)Adsorption states of alkali metal ions in three kinds of 2:1 type clay minerals are systematically investigated via first-principles-based metadynamics. Our reconstructed free energy surfaces in a two dimensional space of coordination numbers specifically employed as collective variables for describing the interlayer cations show that an inner-sphere (IS) complex is preferentially formed for Cs in the 2:1 type trioctahedral clay minerals with saponitelike compositions, where lighter alkali ions show a tendency to form an outer-sphere one instead. The strong preference for an IS complex observed for Cs
in the 2:1 type trioctahedral clay minerals with saponitelike compositions, where lighter alkali ions show a tendency to form an outer-sphere one instead. The strong preference for an IS complex observed for Cs is found to result partially from the capability of recognizing selectively Cs
is found to result partially from the capability of recognizing selectively Cs ions at basal O atoms with the Lewis basicity significantly enhanced by the isomorphic substitution in tetrahedral sheets.
ions at basal O atoms with the Lewis basicity significantly enhanced by the isomorphic substitution in tetrahedral sheets.
Yamada, Hirohisa*; Yokoyama, Shingo*; Watanabe, Yujiro*; Suzuki, Masaya*; Suzuki, Shinichi; Hatta, Tamao*
Nihon Ion Kokan Gakkai-Shi, 25(4), p.207 - 211, 2014/11
Sugikawa, Susumu; Umeda, Miki; Kobayashi, Fuyumi; Nagata, Masanobu*; Dojiri, Shigeru; Amano, Masae*
Proceedings of International Conference on Nuclear Energy System for Future Generation and Global Sustainability (GLOBAL 2005) (CD-ROM), 4 Pages, 2005/10
The mineralization of radioactive contaminated organic wastes by mediated electrochemical oxidation process has some attractive features as alternative to incineration process: The process operates safely at low temperatures and ambient pressures. JAERI has been investigated the process since 1996 and confirmed complete mineralization of this organic solvent. In order to greatly improve current efficiency for the oxidation reaction, further experiments were performed under condition of strong mixing of organic solvent and anolyte with an aide of ultrasonic wave. The current efficiencies for the oxidation reaction by ultrasonic agitation between organic solvent and anolyte were twice to that by mechanical agitation. On the basis of these results, two processes, one for destruction of a small amount of TBP/dodecane and the other for destruction of intermediate compounds following alkaline hydrolysis of a large amount of TBP/dodecane, were proposed.
Kozai, Naofumi; Mitamura, Hisayoshi; Onuki, Toshihiko; Sakai, Takuro; Sato, Takahiro; Oikawa, Masakazu*
Nuclear Instruments and Methods in Physics Research B, 231(1-4), p.530 - 535, 2005/04
Times Cited Count:9 Percentile:55.97(Instruments & Instrumentation)Applicability of micro-PIXE analysis to quantitative evaluation of heavy elements sorbed on minerals was investigated to get better understanding of sorption and distribution of heavy elements onto mixture of minerals in soil. For this, external standards, that is, heavy element-sorbing minerals of uniform shape and size, were analyzed by micro-PIXE. It was found that such external standards were available to quantitative evaluation by micro-PIXE though their applicability may be limited.